Classes- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
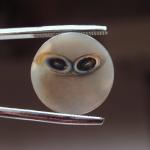
| Hardness : 7 Specific Gravity : 2.61 Refractive index : 1.53 - 1.5 Doubly Refracting (bi-refraction) : 0.004 Most agates occur as nodules in volcanic rocks or ancient lavas where they represent cavities originally produced by the disengagement of volatiles in the molten mass which were then filled, wholly or partially, by siliceous matter deposited in regular layers upon the walls. Such agates, when cut transversely, exhibit a succession of parallel lines, often of extreme tenuity, giving a banded appearance to the section. Such stones are known as banded agate, riband agate and striped agate. In the formation of an ordinary agate, it is probable that waters containing silica in solution -- derived, perhaps, from the decomposition of some of the silicates in the lava itself -- percolated through the rock and deposited a siliceous coating on the interior of the vapour-vesicles. Variations in the character of the solution or in the conditions of deposit may cause corresponding variation in the successive layers, so that bands of chalcedony often alternate with layers of crystalline quartz. Several vapour-vesicles may unite while the rock is viscous, and thus form a large cavity which may become the home of an agate of exceptional size; thus a Brazilian geode lined with amethyst and weighing 35 tons was exhibited at the Dusseldorf Exhibition of 1902. The first deposit on the wall of a cavity, forming the "skin" of the agate, is generally a dark greenish mineral substance, like celadonite, delessite or "green earth," which are rich in iron probably derived from the decomposition of the augite in the enclosing volcanic rock. This green silicate may give rise by alteration to a brown iron oxide (limonite), producing a rusty appearance on the outside of the agate-nodule. The outer surface of an agate, freed from its matrix, is often pitted and rough, apparently in consequence of the removal of the original coating. The first layer spread over the wall of the cavity has been called the "priming," and upon this base zeolitic minerals may be deposited. Many agates are hollow, since deposition has not proceeded far enough to fill the cavity, and in such cases the last deposit commonly consists of quartz, often amethyst, having the apices of the crystals directed towards the free space so as to form a crystal-lined cavity, or geode. On the disintegration of the matrix in which the agates are embedded, they are set free. The agates are extremely resistant to weathering and remain as nodules in the soil or are deposited as gravel in streams and shorelines.
Types of agate Turritella agate is formed from fossil Turritella shells silicified in a chalcedony base. Turritella are spiral marine gastropods having elongated, spiral shells composed of many whorls. Similarly, coral, petrified wood and other organic remains or porous rocks can also become agatized. Agatized coral is often referred to as Petoskey agate or stone. Certain stones, when examined in thin sections by transmitted light, show a diffraction spectrum due to the extreme delicacy of the successive bands, whence they are termed rainbow agates. Often agate coexists with layers or masses of opal, jasper or crystalline quartz due to ambient variations during the formation process. Other forms of agate include carnelian agate (usually exhibiting reddish hues), Botswana agate, Ellensburg blue agate, blue lace agate, plume agate (such as Carey, Graveyard Point, Sage, St. Johns, Teeter Ranch and others), tube agate (with visible flow channels), fortification agate (which exhibit little or no layered structure), fire agate (which seems to glow internally like an opal) and Mexican crazy-lace agate (which exhibits an often brightly colored, complex banded pattern). Agate beliefsIn many traditions agate is believed to cure the stings of scorpions and the bites of snakes, soothe the mind, prevent contagion, still thunder and lightning, promote eloquence, secure the favor of the powerful, and bring victory over enemies. Persian magi are also known to have prized agate rings in their work and beliefs. Uses in industryIndustry uses agates chiefly to make ornaments such as pins, brooches, paper knives, inkstands, and seals. Because of its hardness and ability to resist acids, agate is used to make mortars and pestles to crush and mix chemicals. |
- Birth Stone Gems
- Wedding & Anniversary Gems
- How To Guides
- Fireable Gems
- Nonprofits and Guilds
- Gem Show
- Gem Stone Information
- ·Abalone
- ·Achroite (Tourmaline)
- ·Agate ( Chalcedony)
- ·Alexandrite
- ·Almandine ( Garnet )
- ·Amber
- ·Amethyst ( Quartz)
- ·Ammolite
- ·Andalusite
- ·Andradite Garnet
- ·Apatite
- ·Aquamarine ( Beryl )
- ·Aventurine ( Quartz )
- ·Azurite
- ·Benitoite
- ·Bloodstone ( Chalcedony )
- ·Brown Quartz ( Smokey Quartz )
- ·Calcite
- ·Carnelian ( Chalcedony )
- ·Cassiterite
- ·Celestine
- ·Cerussite
- ·Chalcedony
- ·Chatoyant Quartz
- ·Chrysoberyl
- ·Chrysocolla
- ·Chrysoprase (Chalcedony)
- ·Citrine ( Quartz )
- ·Coral
- ·Danburite
- ·Diamond
- ·Diopside
- ·Dioptase
- ·Dravite ( Tourmaline)
- ·Emerald ( Beryl )
- ·Enstatite
- ·Epidote
- ·Euclase
- ·Fire Agate (Chalcedony)
- ·Fluorite
- ·Gold
- ·Goshenite (Beryl)
- ·Grossular Garnet (Tsavorite Garnet)
- ·Gypsum
- ·Heliodor ( Beryl )
- ·Hematite
- ·Hessonite (Grossular Garnet)
- ·Imperial Topaz
- ·Indicolite ( Tourmaline)
- ·Iolite
- ·Ivory
- ·Jadeite
- ·Jasper (Chalcedony)
- ·Jet
- ·Kornerupine
- ·Kunzite
- ·Kyanite
- ·Labradorite
- ·Lapis Lazuli ( Lazurite)
- ·Lazulite
- ·Malachite
- ·Meerschaum
- ·Microcline
- ·Milky Quartz
- ·Moonstone
- ·Morganite ( Beryl)
- ·Nephrite ( Jade)
- ·Obsidian
- ·Oligoclase
- ·Onyx
- ·Opal
- ·Orthoclase
- ·Padparasha ( Corundum)
- ·Pearl
- ·Peridot
- ·Pink Topaz ( Mercury Myst Vapor )
- ·Plasma ( Chalcedony)
- ·Prase ( Chalcedony )
- ·Prehnite
- ·Pyrite
- ·Pyrope ( Garnet )
- ·Rock Crystal ( Quartz )
- ·Rubellite ( Tourmaline)
- ·Ruby ( Corundum)
- ·Sapphire ( Corundum)
- ·Sardonyx ( Chalcedony)
- ·Scapolite
- ·Schorl (Tourmaline)
- ·Shell
- ·Spessarite (Garnet)
- ·Sphalerite
- ·Spinel
- ·Spodumene (Hiddenite - Triphane)
- ·Tanzanite (Zoisite)
- ·Tektites ( Moldavite )
- ·Tiger Eye
- ·Titanite (Sphene)
- ·Topaz
- ·Turquoise
- ·YAG (Garnet)
- ·Zircon